Social marketing has evolved from simple posting and promotion into a structured discipline that shapes how organizations influence behavior, build trust, and create measurable business impact. Today, brands are not just competing for attention—they are competing for relevance, credibility, and emotional connection. Social marketing sits at the center of this transformation, combining psychology, technology, storytelling, and data.
Consider a small fitness studio owner named Petra in Brno. Initially, Petra posted occasional photos of workouts on social platforms, hoping to attract new clients. Engagement remained low, and growth was slow. After implementing a structured social marketing approach—defining her audience, crafting educational content, and measuring engagement—her studio grew membership by 64% within eight months. Petra did not simply post more; she adopted a strategic social marketing framework that aligned communication with audience needs.
This shift reflects a broader trend. Consumer trust increasingly depends on consistent social presence, with global trust research showing that 63% of people trust information from brands they follow regularly. Social marketing is no longer optional—it is a core business function.
Article Outline
- Definition and meaning of social marketing
- Importance and business impact
- Professional framework overview
- Core structural components
- Professional implementation principles
What Is Social Marketing

Social marketing is the strategic use of social platforms, behavioral insights, and targeted communication to influence audience perceptions, decisions, and actions. It focuses on building relationships and guiding audience behavior over time rather than pushing immediate sales.
Unlike traditional advertising, which interrupts audiences, social marketing integrates into daily digital habits. It creates value through useful information, entertainment, emotional resonance, and consistent engagement.
At its core, social marketing combines three essential elements:
- Audience understanding — knowing motivations, fears, goals, and habits
- Strategic communication — delivering the right message at the right time
- Behavior influence — guiding actions such as purchasing, subscribing, or sharing
For example, a SaaS company targeting freelancers may publish educational content about productivity challenges, gradually positioning its software as a natural solution. Instead of aggressive promotion, the company builds trust first, then converts that trust into adoption.
Social marketing is not defined by platforms like Instagram, LinkedIn, or TikTok. It is defined by strategy, structure, and intent. Platforms are simply distribution channels.
Why Social Marketing Matters
The importance of social marketing stems from how people make decisions. Modern consumers research, compare, and evaluate before committing. Social platforms serve as discovery engines, validation sources, and trust signals.
Decision-making increasingly depends on exposure and familiarity. Behavioral psychology shows that repeated exposure increases trust and perceived authority. This phenomenon, often called the familiarity effect, explains why consistent social marketing builds brand preference.
A practical example illustrates this clearly. Tomas, a freelance web developer, regularly shared short educational posts explaining common website mistakes. Over time, his audience began viewing him as an authority. When businesses needed help, they naturally contacted him—even without direct advertising. His social marketing established credibility before the sales conversation began.
The business impact of social marketing includes measurable outcomes:
- Brand awareness growth through repeated exposure
- Trust development through consistent value delivery
- Customer acquisition through relationship building
- Customer retention through ongoing engagement
- Market positioning through expertise demonstration
Organizations that invest in structured social marketing often experience accelerated growth because they reduce friction in the decision process. Instead of convincing cold audiences, they nurture warm, familiar ones.
This explains why global digital reports show over 5 billion social media users worldwide. Social marketing enables organizations to access, influence, and serve this massive audience efficiently.
Framework Overview
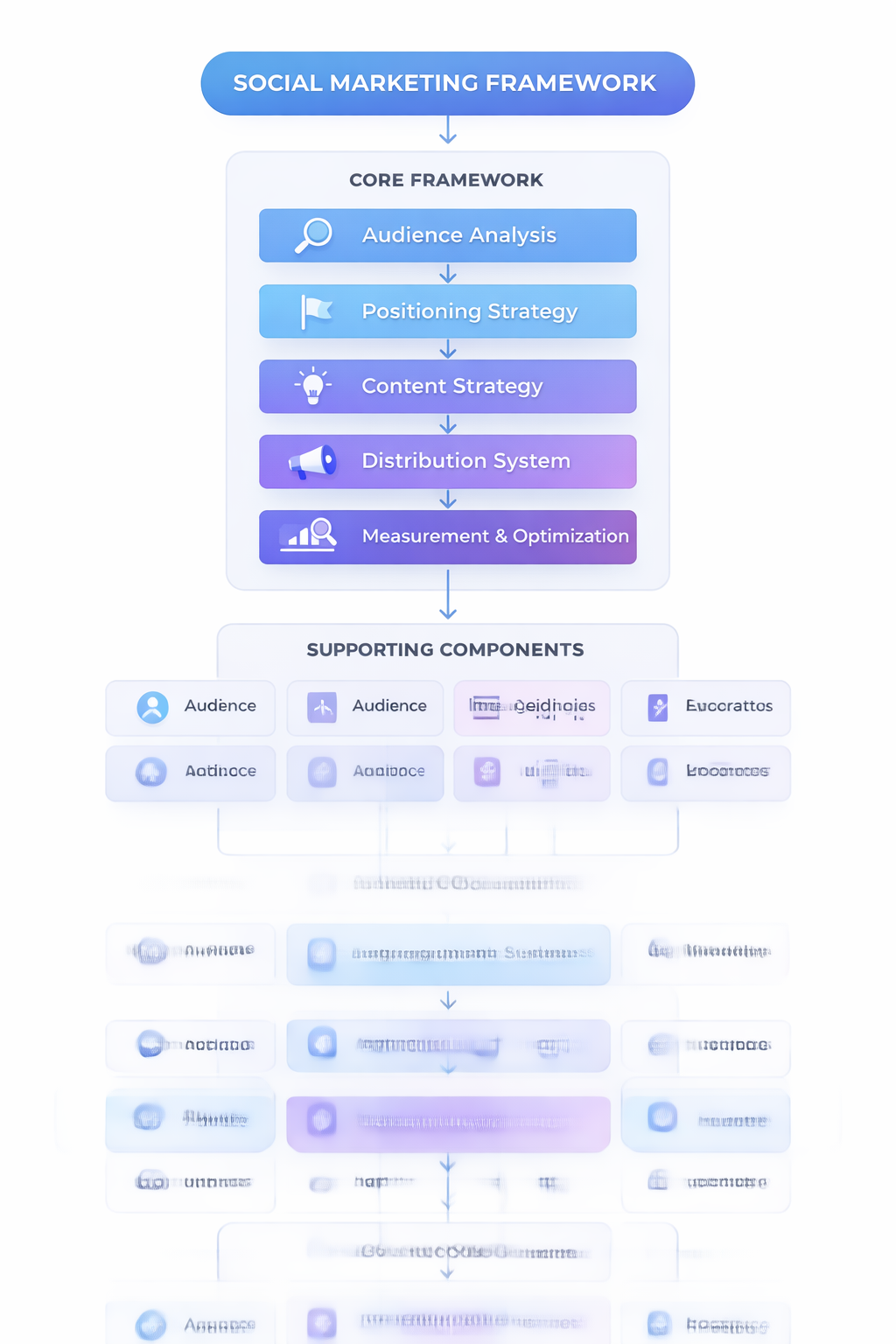
Professional social marketing operates through a structured framework rather than random activity. This framework ensures consistency, efficiency, and measurable results.
The framework typically follows five sequential layers:
- Audience analysis — defining who the audience is and what they need
- Positioning strategy — defining how the brand should be perceived
- Content strategy — designing content aligned with audience needs
- Distribution system — delivering content consistently through channels
- Measurement and optimization — improving performance based on data
Each layer builds on the previous one. Without audience analysis, positioning becomes unclear. Without positioning, content becomes generic. Without content, distribution becomes meaningless.
Consider an e-commerce brand selling sustainable clothing. Instead of posting product images randomly, the brand creates educational content about sustainability, shares manufacturing transparency, and highlights environmental impact. This strategic framework strengthens positioning and attracts aligned customers.
The framework transforms social marketing from reactive posting into proactive growth infrastructure.
Core Components
Social marketing consists of interconnected components that function together as a system. Each component serves a specific role in influencing audience perception and behavior.
1. Audience Intelligence
This component focuses on understanding audience psychology, including motivations, fears, aspirations, and decision triggers. Audience intelligence allows organizations to create relevant and resonant communication.
2. Content Architecture
Content architecture defines content categories, themes, and messaging structure. Instead of random posts, content aligns with strategic goals such as education, trust building, and conversion preparation.
For example, a cybersecurity company may structure content into:
- Educational posts explaining threats
- Case studies demonstrating solutions
- Authority content showcasing expertise
- Trust content featuring customer success
3. Distribution Consistency
Consistency reinforces familiarity. Irregular activity weakens trust signals, while consistent presence strengthens perceived reliability.
Organizations that maintain regular communication remain visible in audience memory, increasing likelihood of future engagement and conversion.
4. Engagement Systems
Engagement transforms passive audiences into active participants. Responding to comments, answering questions, and participating in conversations strengthens relationships.
This interaction builds emotional connection and loyalty, which are difficult for competitors to replicate.
5. Performance Measurement
Measurement identifies what works and what does not. Metrics such as engagement rate, reach, conversion rate, and audience growth provide insight into effectiveness.
Measurement enables optimization, ensuring continuous improvement.
Professional Implementation
Professional social marketing implementation requires systematic execution rather than improvisation. Organizations must treat social marketing as infrastructure, not a side activity.
Implementation begins with strategic clarity. Organizations must define:
- Target audience segments
- Desired positioning
- Content themes and messaging
- Distribution frequency
- Performance indicators
Once defined, execution becomes predictable and scalable.
A practical example illustrates this clearly. A software startup targeting accountants defined its positioning as an efficiency expert. Instead of promoting software features directly, it published educational content about workflow automation. Accountants began associating the brand with productivity improvement. When evaluating software options, the startup naturally appeared as the preferred choice.
This demonstrates a critical principle: social marketing shapes perception before purchase intent exists.
Professional implementation also requires patience. Social marketing operates as a compounding system. Early efforts build visibility, which builds familiarity, which builds trust, which ultimately builds conversions.
Organizations that approach social marketing strategically create sustainable competitive advantage. Their visibility, credibility, and audience relationships strengthen continuously, making growth more efficient over time.
This foundation sets the stage for deeper exploration of social marketing strategy, systems, and optimization in the following sections.
Step By Step Implementation

Implementing social marketing successfully requires a structured sequence of actions. Organizations that follow systematic implementation build predictable growth systems, while those that improvise often experience inconsistent results.
The first step is defining precise audience segments. Broad targeting reduces effectiveness, while focused targeting improves relevance and engagement. Businesses that segment audiences effectively generate up to 760% increase in revenue from segmented campaigns, demonstrating the value of precise audience definition.
Lucie, founder of a productivity SaaS startup, initially targeted “entrepreneurs” broadly. Her messaging failed to resonate. After narrowing her audience to freelance designers, engagement increased significantly. Her content addressed specific workflow pain points, leading to a 3.4x increase in inbound leads.
The second step involves defining positioning. Positioning determines how audiences perceive the brand relative to alternatives. Clear positioning simplifies decision-making for potential customers.
Positioning effectiveness directly impacts growth, as consistent branding across channels increases revenue by up to 23%. Consistent perception reinforces credibility.
The third step is building a structured content system. Content must align with audience needs and strategic positioning. Educational, trust-building, and authority-driven content creates sustainable influence.
Content consistency drives results because audiences require repeated exposure before acting. Most consumers require multiple brand interactions before making purchase decisions, reinforcing the importance of sustained communication.
The fourth step involves establishing publishing infrastructure. Content must be distributed consistently across relevant platforms. Businesses that publish consistently experience significantly stronger engagement compared to inconsistent publishers.
The fifth step is implementing engagement processes. Engagement strengthens relationships and increases audience loyalty. Responding to comments, answering questions, and participating in conversations improves trust signals.
The final step is implementing measurement systems. Measurement enables continuous optimization and performance improvement. Companies using structured analytics improve marketing ROI significantly, as data-driven organizations are 23 times more likely to outperform competitors.
This structured sequence transforms social marketing into a scalable growth system.
Execution Layers
Social marketing implementation operates across multiple execution layers. Each layer contributes to long-term effectiveness.
Strategic Layer
This layer defines long-term direction. It includes audience targeting, positioning, and messaging architecture. Without strategic clarity, tactical execution becomes inefficient.
Strategic clarity improves performance significantly, especially when organizations align messaging with audience motivations. Customer-centric brands achieve 40% more revenue growth than competitors lacking personalization.
Martin, a cybersecurity consultant, refined his strategic layer by targeting fintech startups specifically. This focus improved engagement and accelerated client acquisition.
Content Layer
The content layer translates strategy into communication. Content must educate, inform, and influence audience perception.
Content quality directly impacts effectiveness. Long-form content generates 77% more backlinks, increasing visibility and authority.
Educational content builds trust over time. Trust-driven content improves conversion probability because audiences prefer credible and knowledgeable providers.
Distribution Layer
The distribution layer ensures content reaches the intended audience. Without effective distribution, even high-quality content remains invisible.
Content distribution effectiveness impacts visibility significantly. Only 5.7% of content achieves strong visibility, highlighting the importance of structured distribution.
Petra improved her distribution layer by focusing on LinkedIn rather than posting randomly across multiple platforms. Concentrated distribution increased her reach and engagement.
Engagement Layer
This layer focuses on audience interaction. Engagement strengthens relationships and reinforces brand credibility.
Customer engagement drives financial performance. Highly engaged customers generate 23% higher profitability, demonstrating engagement’s business impact.
Measurement Layer
This layer monitors performance and identifies improvement opportunities. Measurement enables strategic evolution.
Performance tracking improves outcomes significantly. Organizations using advanced analytics improve decision-making accuracy and overall marketing efficiency.
Optimization Process
Optimization transforms social marketing from static execution into adaptive growth infrastructure. Continuous optimization improves performance over time.
The first optimization phase focuses on performance analysis. This involves identifying high-performing content patterns. Content optimization improves engagement and conversion potential.
High-performing content typically aligns with audience needs and interests. Content relevance significantly influences performance, as personalized experiences improve engagement rates dramatically.
The second phase involves experimentation. Testing different formats, topics, and messaging identifies optimal strategies.
Experimentation is essential because even small improvements compound over time. Conversion optimization improvements of just 1% can significantly increase revenue at scale.
The third phase involves scaling successful content. Scaling amplifies impact by increasing exposure of proven content.
Scaling effectiveness increases reach efficiency. Video content, for example, generates 92% audience reach among internet users, making it one of the most effective scalable formats.
The final phase involves continuous iteration. Social marketing effectiveness improves progressively through refinement.
Organizations that continuously optimize outperform static competitors because they adapt to audience preferences.
Implementation Stories
Real-world implementation demonstrates how structured social marketing drives growth.
David, founder of an AI analytics platform, struggled to generate awareness. His team implemented a structured social marketing system focused on educational content explaining AI use cases.
Initially, engagement remained modest. However, after six months of consistent execution, audience growth accelerated. Educational content positioned his company as an authority, increasing inbound inquiries significantly.
This pattern reflects broader behavioral trends, as trust influences decision-making strongly. Buyers are more likely to choose brands they recognize and trust.
Another example involves Anna, a marketing consultant serving e-commerce businesses. She implemented structured content themes focusing on customer acquisition strategies.
Her consistent content attracted business owners facing growth challenges. Over time, her audience became a reliable source of inbound leads.
This growth pattern aligns with broader digital adoption trends, as over 63% of the global population uses social media, creating massive opportunity for visibility and influence.
Structured implementation transformed her social marketing into a predictable client acquisition system.
Statistics And Data

Social marketing performance becomes predictable when guided by measurable data. Analytics transforms assumptions into evidence, allowing organizations to identify growth drivers, eliminate inefficiencies, and scale effective strategies.
Digital behavior has shifted heavily toward social ecosystems, with over 5.04 billion people actively using social media globally. This scale creates unprecedented opportunities for targeted audience engagement and growth.
Content reach and engagement patterns reveal how audiences interact with brands. Video content dominates engagement, as 92% of internet users consume online video content, making video a central component of modern social marketing.
Engagement metrics provide insight into audience relationships. High engagement signals trust and relevance. Engagement-driven customers deliver greater long-term value, with emotionally connected customers generating 306% higher lifetime value.
Reach and impressions measure visibility, while engagement metrics measure influence. Visibility without engagement indicates weak audience connection, while strong engagement signals effective messaging.
Conversion metrics provide deeper insight into business impact. Conversion-driven social marketing directly supports revenue growth, as businesses prioritizing customer experience achieve 40% higher revenue growth.
Consistency also affects performance outcomes. Brands maintaining consistent presence strengthen audience familiarity and credibility. Familiar brands benefit from increased conversion efficiency due to reduced decision friction.
Mobile accessibility further amplifies social marketing reach. Mobile devices account for over 58% of global website traffic, reinforcing the importance of mobile-optimized content.
Algorithm-driven visibility makes performance measurement essential. Platforms prioritize engaging content, rewarding brands that consistently produce valuable communication.
Understanding data patterns allows organizations to refine strategy and improve outcomes continuously.
Performance Benchmarks
Performance benchmarks provide reference points for evaluating effectiveness. Without benchmarks, organizations cannot determine whether performance meets expectations.
Engagement rate is one of the most important indicators. Typical engagement rates vary by platform, but optimized content consistently outperforms average performance.
Higher engagement improves algorithmic visibility. Content with strong engagement receives greater organic distribution, amplifying reach without additional cost.
Click-through rates provide insight into content effectiveness. High-performing content generates significantly higher click-through rates, with top-performing digital content achieving 27.6% average click-through rate.
Audience growth rate measures long-term brand expansion. Consistent growth indicates effective positioning and communication.
Conversion rate benchmarks measure business impact. Optimized conversion strategies significantly improve acquisition efficiency, as conversion optimization can increase revenue without increasing traffic.
Retention metrics provide insight into audience loyalty. Retention reflects relationship strength and long-term brand value.
Benchmark comparisons allow marketers to identify performance gaps and improvement opportunities.
Organizations that track benchmarks systematically achieve stronger growth consistency and performance predictability.
Analytics Interpretation
Analytics interpretation transforms raw data into actionable insight. Understanding what metrics mean allows marketers to make informed strategic decisions.
High reach combined with low engagement indicates content misalignment with audience interests. This scenario suggests the need to adjust messaging or targeting.
High engagement combined with low conversion indicates strong interest but weak conversion pathways. Improving calls-to-action or conversion infrastructure resolves this issue.
Low reach combined with high engagement indicates strong content quality but limited visibility. Increasing distribution improves growth potential.
High reach and high engagement represent optimal performance conditions. This scenario indicates effective strategy alignment.
Interpretation accuracy improves with experience and structured analysis. Organizations using analytics-driven decision-making improve marketing effectiveness significantly, as data-driven organizations are 23 times more likely to acquire customers.
Analytics interpretation also identifies content patterns. Identifying patterns allows marketers to replicate success consistently.
Audience behavior patterns reveal preferences, motivations, and decision triggers.
Professional marketers use analytics interpretation to guide continuous optimization.
Case Stories
Real-world examples demonstrate how analytics transforms social marketing performance.
Daniel, founder of a fintech startup, initially struggled to grow his audience. His analytics revealed that technical product posts generated low engagement, while educational financial literacy posts performed significantly better.
He shifted his content strategy toward education, explaining financial concepts and industry trends. Within nine months, his audience grew significantly, and inbound partnership inquiries increased.
This shift reflected broader engagement patterns, as educational content improves audience trust and authority perception.
Another example involves Eva, an e-commerce entrepreneur selling wellness products. Her analytics revealed that video demonstrations generated significantly higher engagement than static images.
She prioritized video content, resulting in improved audience engagement and conversion rates. This aligns with broader behavior patterns, as video improves user understanding and trust.
Her success illustrates how analytics-driven strategy improves performance predictability.
Similarly, consulting firms applying structured analytics frameworks consistently improve acquisition efficiency. Firms prioritizing customer experience outperform competitors significantly.
Analytics-driven organizations continuously refine their strategies based on measurable evidence.
Professional Promotion
Professional social marketing promotion requires strategic amplification of high-performing content. Promotion ensures content reaches the most relevant audiences.
Promotion effectiveness increases when based on analytics insights. Amplifying proven content improves return on investment.
Paid promotion accelerates visibility, while organic promotion builds sustainable growth.
Promotion efficiency improves when aligned with audience behavior patterns. Understanding when audiences are active increases engagement probability.
Audience targeting significantly improves promotion effectiveness. Targeted promotion reduces wasted resources and improves conversion rates.
Professional promotion strategies integrate analytics, content strategy, and audience targeting.
Organizations that combine analytics-driven optimization with structured promotion build scalable growth systems.
Analytics transforms social marketing from uncertain experimentation into predictable, measurable business infrastructure.
Future Trends
Social marketing is entering a phase defined by intelligence, automation, and ecosystem integration. The next evolution is not simply about publishing content but building adaptive systems that learn, optimize, and scale continuously. Organizations that prepare for these trends will gain disproportionate advantages in visibility, authority, and acquisition efficiency.
Artificial intelligence is becoming a core component of social marketing infrastructure. AI-powered personalization improves engagement and relevance, with personalization increasing revenue by up to 40%. Intelligent systems analyze audience behavior and optimize content delivery automatically.
Jakub, a SaaS founder in Warsaw, implemented AI-assisted content analysis to identify patterns in engagement. The system revealed that technical tutorials published on Tuesdays generated significantly higher engagement. Adjusting his publishing schedule increased reach by over 60% within three months.
Short-form video continues dominating content consumption patterns. Video-based social marketing drives stronger engagement because it communicates information faster and more effectively. Mobile video consumption continues rising, as 92% of internet users watch video content regularly.
Another major trend is ecosystem integration. Social marketing is no longer isolated—it connects with search, email, content marketing, and conversion infrastructure. Integrated ecosystems improve acquisition efficiency and strengthen audience relationships.
Trust will remain the most valuable currency. Trust-driven brands consistently outperform competitors, especially as digital audiences become more selective.
Professional marketers preparing for future trends often refine systems using structured methodologies found in advanced social marketing ecosystem frameworks.
Strategic Framework Recap
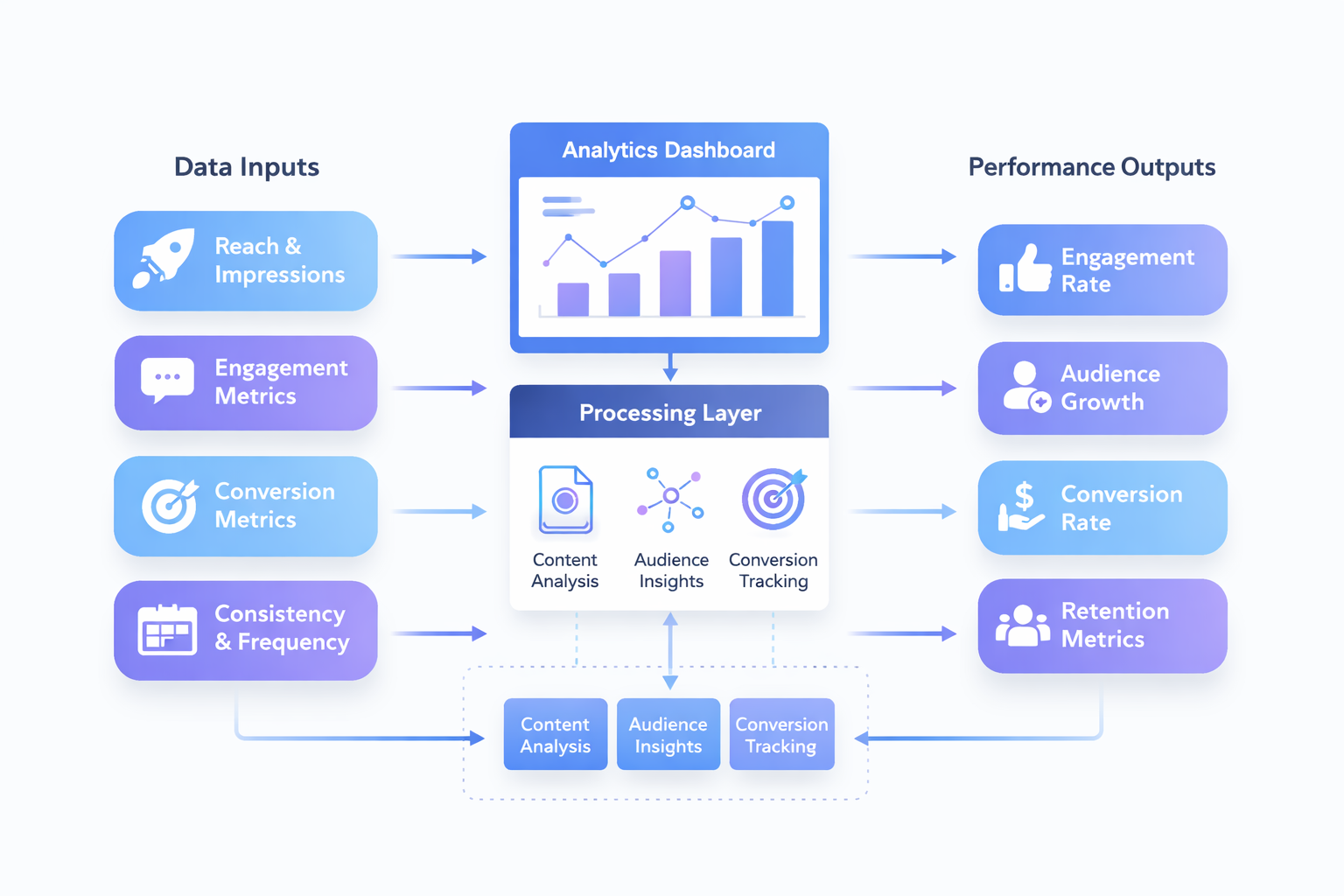
The social marketing framework operates as a structured ecosystem connecting strategy, execution, analytics, and scaling. Each component reinforces the others, creating compounding growth over time.
The framework begins with audience intelligence. Understanding motivations, behavior, and decision triggers allows organizations to create relevant communication.
Next comes strategic positioning. Positioning defines perception and determines how audiences evaluate credibility and expertise.
Content systems transform positioning into communication. Consistent, high-value content builds authority and strengthens trust.
Distribution systems ensure visibility. Even the highest-quality content requires structured distribution to reach intended audiences.
Analytics systems monitor performance and identify improvement opportunities. Data-driven optimization improves efficiency and scalability.
Scaling systems expand reach and automate workflows, allowing growth without proportional increases in effort.
This ecosystem approach transforms social marketing into a self-reinforcing growth infrastructure.
Organizations implementing ecosystem-based systems achieve superior performance, especially as digital adoption continues increasing globally, with over 5 billion social media users actively participating in digital ecosystems.
Framework-driven social marketing enables predictable, scalable, and sustainable growth.
FAQ – Built For Complete Guide
1. How long does social marketing take to produce results?
Initial engagement improvements often appear within 30 to 90 days. Sustainable growth typically develops over 6 to 12 months as trust, visibility, and audience relationships strengthen.
2. What is the most important factor in social marketing success?
Consistency is the most critical factor. Regular communication reinforces familiarity and trust, which influence decision-making and conversion probability.
3. How often should businesses publish content?
Most successful organizations publish between 3 and 5 times per week. Consistent publishing improves visibility and accelerates audience growth.
4. Which platform is best for social marketing?
The best platform depends on audience behavior. LinkedIn works best for B2B audiences, while Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube perform strongly for visual and consumer-focused content.
5. Can small businesses compete with large companies?
Yes. Social marketing rewards relevance and consistency more than size. Smaller organizations often outperform larger competitors through specialized positioning.
6. What type of content performs best?
Educational, story-driven, and authority-building content consistently performs best. Content that solves audience problems generates the strongest engagement.
7. How important is engagement?
Engagement strengthens audience relationships and improves visibility. Highly engaged audiences convert more frequently and remain loyal longer.
8. Is paid promotion necessary?
Paid promotion accelerates growth but is not required. Strong organic strategy builds sustainable growth, while paid promotion amplifies results.
9. How is performance measured?
Performance is measured through engagement rate, audience growth, conversion rate, and audience retention metrics.
10. Can social marketing work for freelancers?
Yes. Freelancers often benefit significantly because social marketing builds authority, attracts clients, and creates predictable inbound opportunities.
11. Why do some social marketing strategies fail?
Failure typically results from inconsistency, lack of positioning, poor audience understanding, or absence of structured systems.
12. Is social marketing still growing?
Yes. Digital adoption continues expanding, and social platforms remain central to modern communication and business growth.
Work With Professionals
Freelancers and independent professionals face a common challenge: finding consistent, high-quality clients. Social marketing builds authority and visibility, but execution requires time, structure, and opportunity alignment. Many talented freelancers struggle not because of lack of skill, but because of limited exposure.
A structured platform solves this challenge by connecting professionals with businesses actively seeking expertise. Instead of chasing clients, freelancers can position themselves where demand already exists.
This approach transforms client acquisition into a predictable system. Freelancers using structured professional platforms gain access to opportunities aligned with their expertise, reducing uncertainty and improving income stability.
Professional ecosystems also strengthen positioning. Being present in trusted networks reinforces credibility and increases selection probability.
Freelancers who combine social marketing authority with professional platforms gain significant competitive advantage. Their visibility attracts inbound clients, while platform presence accelerates discovery.
Building a sustainable freelance business requires both authority and access. Authority attracts attention. Access converts attention into opportunities.

